APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) are the invisible glue that allows different software systems to communicate with each other. Every time you check the weather on your phone, make an online payment, log in using Google, or sync business apps. an API is working behind the scenes.
In today’s connected world, APIs are not just technical tools; they are business enablers.
What Is an API?
An API (Application Programming Interface) is a set of rules that allows one software application to interact with another.
Think of an API as a waiter in a restaurant:
- You (the client) place an order
- The waiter (API) delivers the request to the kitchen (server/system)
- The waiter brings back your food (response)
You don’t need to know how the kitchen works — you just get what you asked for.
How APIs Work (Step by Step)
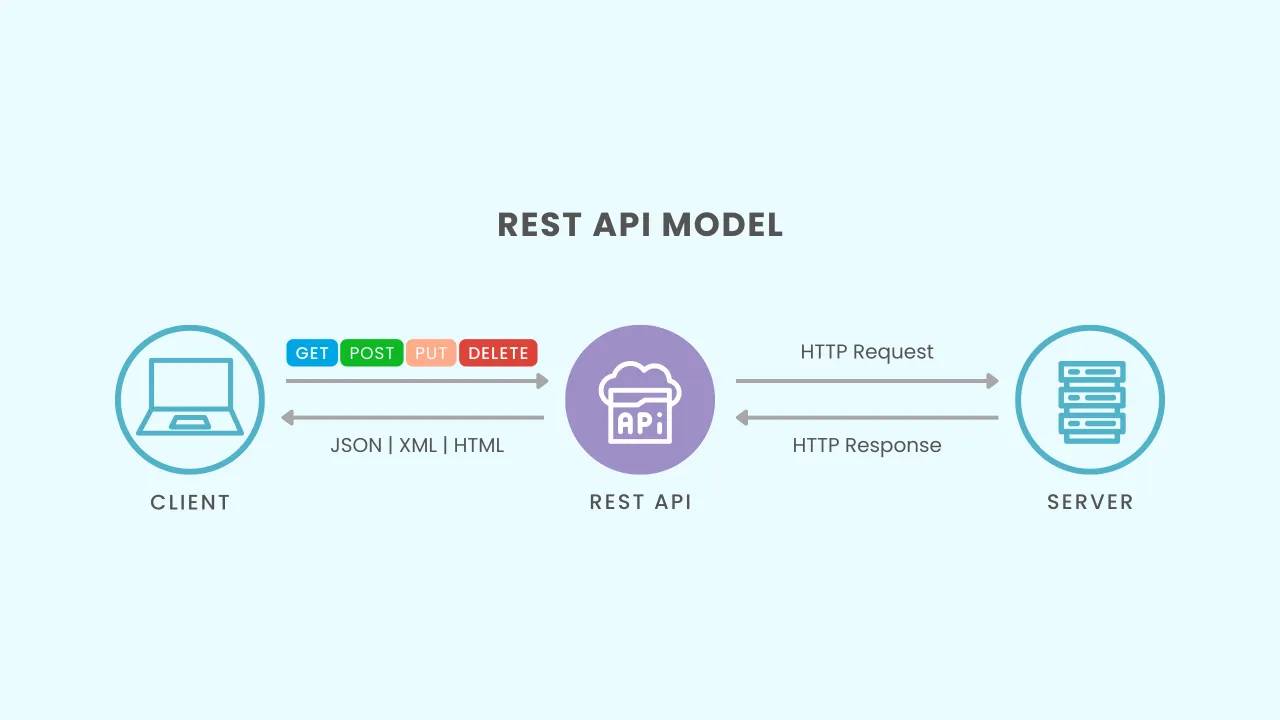
1. Request Initiation
A client (mobile app, web app, or browser) sends a request to an API endpoint — a specific URL that represents a function or resource.
Example:
GET https://api.store.com/orders/123
2. Processing
The API server receives the request and:
- Validates authentication
- Checks permissions
- Processes business logic
- Communicates with databases or other services
3. Response
The API returns a structured response, usually in JSON or XML format.
Example JSON response:
{ "order_id": 123, "status": "shipped", "total": 250.00 }
Common Types of APIs
| Type | Description | Example Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| REST API | Most common, uses HTTP methods | Web & mobile apps |
| SOAP API | Protocol-based, strict structure | Banking & enterprise systems |
| GraphQL | Flexible queries for data | Modern web apps |
| Webhooks | Event-driven API calls | Payment notifications |
Why API Documentation Matters
An API without documentation is like a machine without instructions. Even a powerful API becomes frustrating if developers don’t know how to use it properly.
Great API documentation reduces integration time, prevents errors, and improves adoption.
What Makes Great API Documentation
✅ Clear Endpoints and Methods
Explain what each URL does and which HTTP method to use.
Example:
GET /api/v1/orders → Fetch orders POST /api/v1/orders → Create order PUT /api/v1/orders/1 → Update order DELETE /api/v1/orders/1 → Delete order
✅ Request and Response Examples
Developers should see real, practical examples including parameters and outputs.
✅ Error Handling
List possible error codes and their meanings.
| Code | Meaning |
|---|---|
| 400 | Bad Request |
| 401 | Unauthorized |
| 403 | Forbidden |
| 404 | Not Found |
| 500 | Server Error |
✅ Authentication Information
Explain clearly how to authenticate:
- API Keys
- OAuth Tokens
- JWT (JSON Web Tokens)
✅ Interactive Testing
Interactive documentation lets developers test APIs directly.

Tools that support this:
- Swagger / OpenAPI
- Postman Collections
- Redoc
Tools That Help You Work With APIs
| Tool | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Postman | Send requests & test APIs |
| Swagger | Design & document APIs |
| cURL | Command-line API interaction |
| Insomnia | Lightweight API testing tool |
| Odoo External APIs | Integrate ERP data with other systems |
Real-World Uses of APIs
APIs power almost everything in modern software:
- Payment gateways
- Shipping integrations
- Email services
- Business intelligence dashboards
- ERP integrations like Odoo
- Automation between apps
If software needs to talk to another system — there’s an API involved.
APIs are the foundation of modern digital ecosystems. They enable seamless integrations, automation, scalability, and innovation.
Whether you’re a developer building custom integrations, an ERP consultant connecting business systems, or a product manager shaping digital strategy, understanding APIs — and the importance of good documentation — is essential.
“Good APIs make products powerful. Great documentation makes them usable.”